I'd like to be able to implement a "capped" cumulative sum in BigQuery using SQL.
Here's what I mean: I have a table whose rows have the amount by which a value is increased/decreased each day, but the value cannot go below 0 or above 100. I want to compute the cumulative sum of the changes to keep track of this value.
As an example, consider the following table:
day | change
--------------
1 | 70
2 | 50
3 | 20
4 | -30
5 | 10
6 | -90
7 | 20
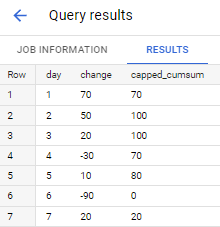
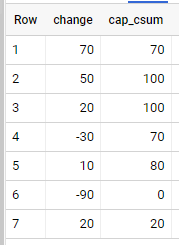
I want to make a column that has the capped cumulative sum so that it looks like this:
day | change | capped cumsum
----------------------------
1 | 70 | 70
2 | 50 | 100
3 | 20 | 100
4 | -30 | 70
5 | 10 | 80
6 | -90 | 0
7 | 20 | 20
Simply doing SUM (change) OVER (ORDER BY day) and capping the values at 100 and 0 won't work. I need some sort of recursive loop and I don't know how to implement this in BigQuery.
Eventually I'd also like to do this over partitions, so that if I have something like
day | class | change
--------------
1 | A | 70
1 | B | 12
2 | A | 50
2 | B | 83
3 | A | -30
3 | B | 17
4 | A | 10
5 | A | -90
6 | A | 20
I can do the capped cumulative sum partitioned over each class.
CodePudding user response:
I need some sort of recursive loop and I don't know how to implement this in BigQuery
Super naïve / cursor based approach
declare cumulative_change int64 default 0;
create temp table temp_table as (
select * , 0 as capped_cumsum from your_table where false
);
for rec in (select * from your_table order by day)
do
set cumulative_change = cumulative_change rec.change;
set cumulative_change = case when cumulative_change < 0 then 0 when cumulative_change > 100 then 100 else cumulative_change end;
insert into temp_table (select rec.*, cumulative_change);
end for;
select * from temp_table order by day;
if applied to sample data in your question - output is
Slightly modified option with use of array instead of temp table
declare cumulative_change int64 default 0;
declare result array<struct<day int64, change int64, capped_cumsum int64>>;
for rec in (select * from your_table order by day)
do
set cumulative_change = cumulative_change rec.change;
set cumulative_change = case when cumulative_change < 0 then 0 when cumulative_change > 100 then 100 else cumulative_change end;
set result = array(select as struct * from unnest(result) union all select as struct rec.*, cumulative_change);
end for;
select * from unnest(result) order by day;
P.S. I like none of above options so far :o)
Meantime, that approach might work for relatively small tables, set of data
CodePudding user response:
Using RECURSIVE CTE can be another option:
DECLARE sample ARRAY<STRUCT<day INT64, change INT64>> DEFAULT [
(1, 70), (2, 50), (3, 20), (4, -30), (5, 10), (6, -90), (7, 20)
];
WITH RECURSIVE ccsum AS (
SELECT 0 AS n, vals[OFFSET(0)] AS change,
CASE
WHEN vals[OFFSET(0)] > 100 THEN 100
WHEN vals[OFFSET(0)] < 0 THEN 0
ELSE vals[OFFSET(0)]
END AS cap_csum
FROM sample
UNION ALL
SELECT n 1 AS n, vals[OFFSET(n 1)] AS change,
CASE
WHEN cap_csum vals[OFFSET(n 1)] > 100 THEN 100
WHEN cap_csum vals[OFFSET(n 1)] < 0 THEN 0
ELSE cap_csum vals[OFFSET(n 1)]
END AS cap_csum
FROM ccsum, sample
WHERE n < ARRAY_LENGTH(vals) - 1
),
sample AS (
SELECT ARRAY_AGG(change ORDER BY day) vals FROM UNNEST(sample)
)
SELECT * EXCEPT(n) FROM ccsum ORDER BY n;
output: