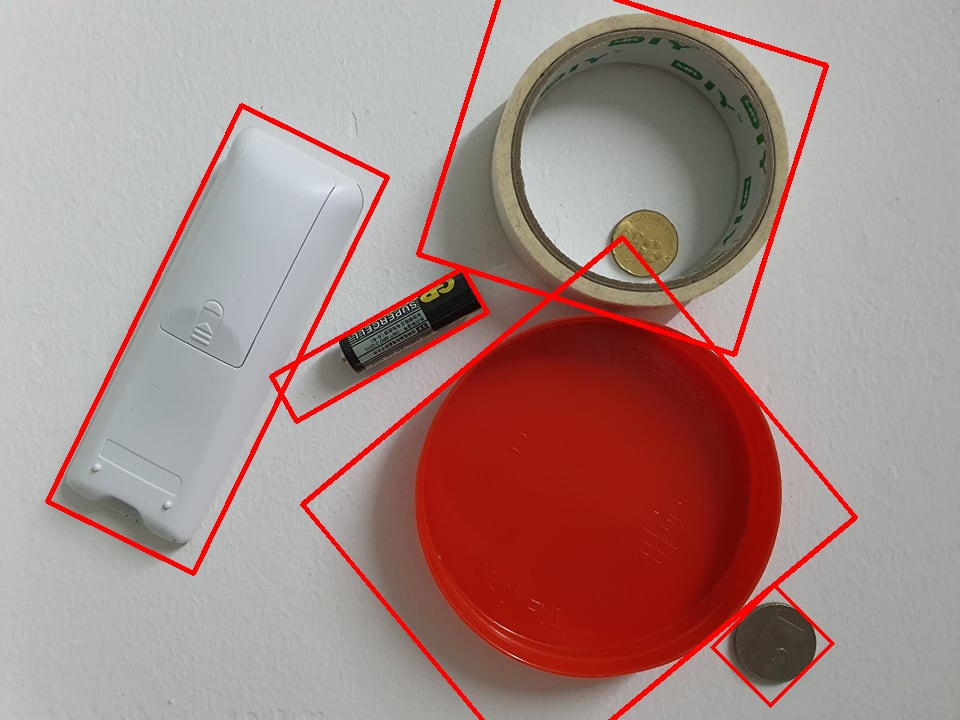
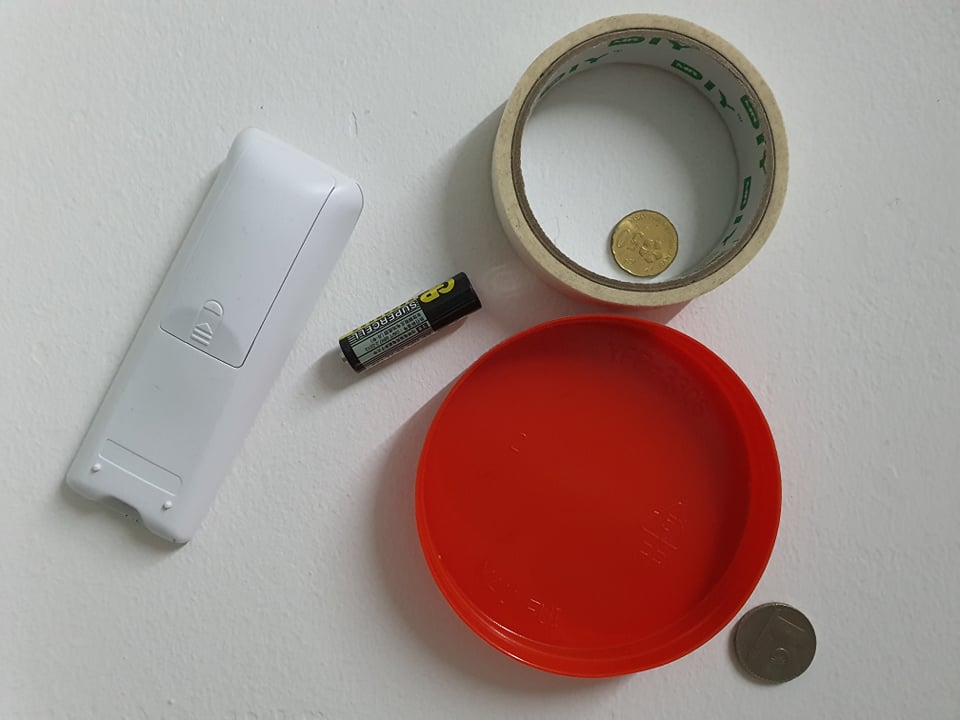
I am a beginner and I am trying to apply an outline to the white remote control on the left that shares the same color with the background.

a = cv2.imread(file_name)
imgGray = cv2.cvtColor(a,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
imgGray = cv2.GaussianBlur(imgGray,(11,11),20)
k5 = np.array([[-1,-1,-1],[-1,9,-1],[-1,-1,-1]])
imgGray = cv2.filter2D(imgGray,-1,k5)
cv2.namedWindow("Control")
cv2.createTrackbar("blocksize","Control",33,1000,f)
cv2.createTrackbar("c","Control",3,100,f)
while True:
strel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_CROSS,(3,3))
blocksize = cv2.getTrackbarPos("blocksize","Control")
c = cv2.getTrackbarPos("c","Control")
if blocksize%2==0:
blocksize = 1
thrash = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(imgGray,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV,blockSize=blocksize,C=c)
thrash1 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(imgGray,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV,blockSize=blocksize,C=c)
cv2.imshow("mean",thrash)
cv2.imshow("gaussian",thrash1)
#r,thrash = cv2.threshold(imgGray,150,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
key = cv2.waitKey(1000)
if key == 32 or iter == -1:
break
edges = cv2.Canny(thrash,100,200)
cv2.imshow('sharpen',sharpen)
cv2.imshow('edges',edges)
cv2.imshow('grey ',imgGray)
cv2.imshow('thrash ',thrash)
cv2.waitKey(0)
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(imgGray,cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT,1,60,param1=240,param2=50,minRadius=0,maxRadius=0)
contours,_ = cv2.findContours(thrash,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
putlabel(circles,a,contours)
Those are what I have tried, I have also tried morphological operation such as dilation, erosion, opening and closing too but I am still unable to acquire the result.
Below is my best result but the noise is too severe and the remote controller didn't get fully outlined.
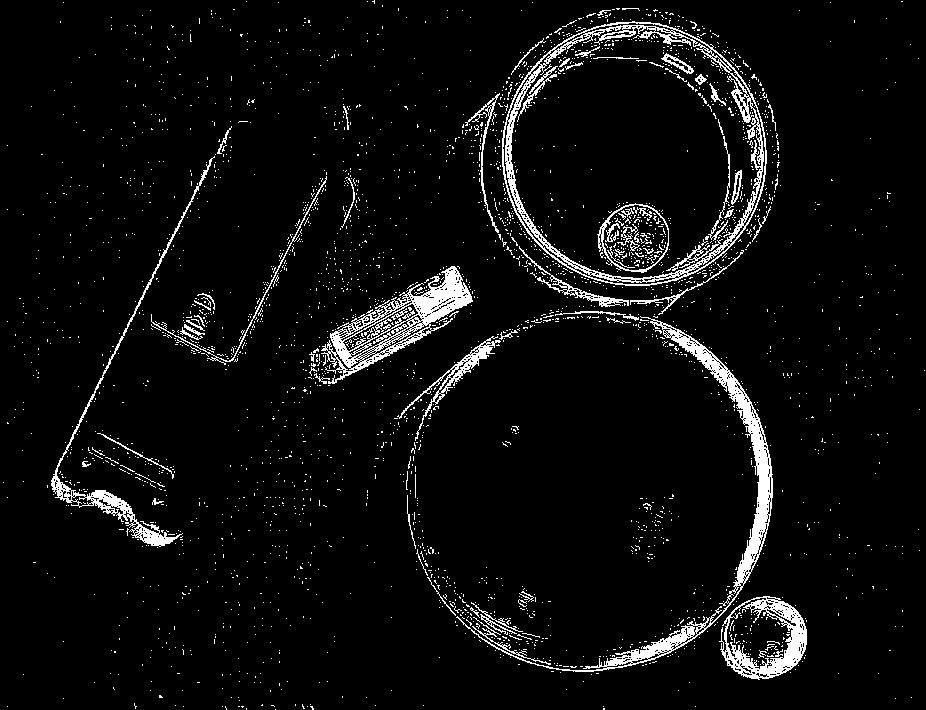
CodePudding user response:
I don't think simple image-processing will be able to isolate an object with the same color as the background. Therefore we have to switch to deep/machine learning. The idea is to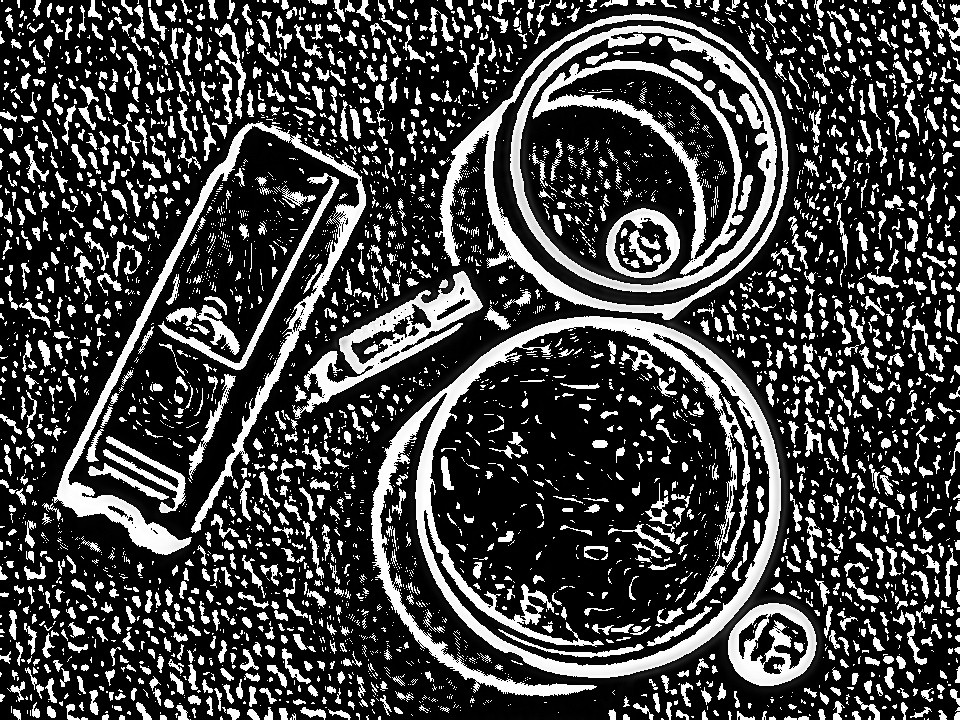 
As you can see, it functions as an edge detector. You can vary the kernel sizes (k1, k2) and sigma values (s1, s2)
# Applying Otsu Threshold and finding contours
th = cv2.threshold(DoG_img ,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(th, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# Create copy of original image
img1 = img.copy()
# for each contour above certain area and extent, draw minimum bounding box
for c in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(c)
if area > 1500:
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(c)
extent = int(area)/w*h
if extent > 2000:
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(c)
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
box = np.int0(box)
cv2.drawContours(img1,[box],0,(0,255,0),4)
As you can see, the result is not perfect. The shadows of the objects are also captured during the edge detection process (Difference of Gaussians). You can try varying the parameters to check if the result gets better.