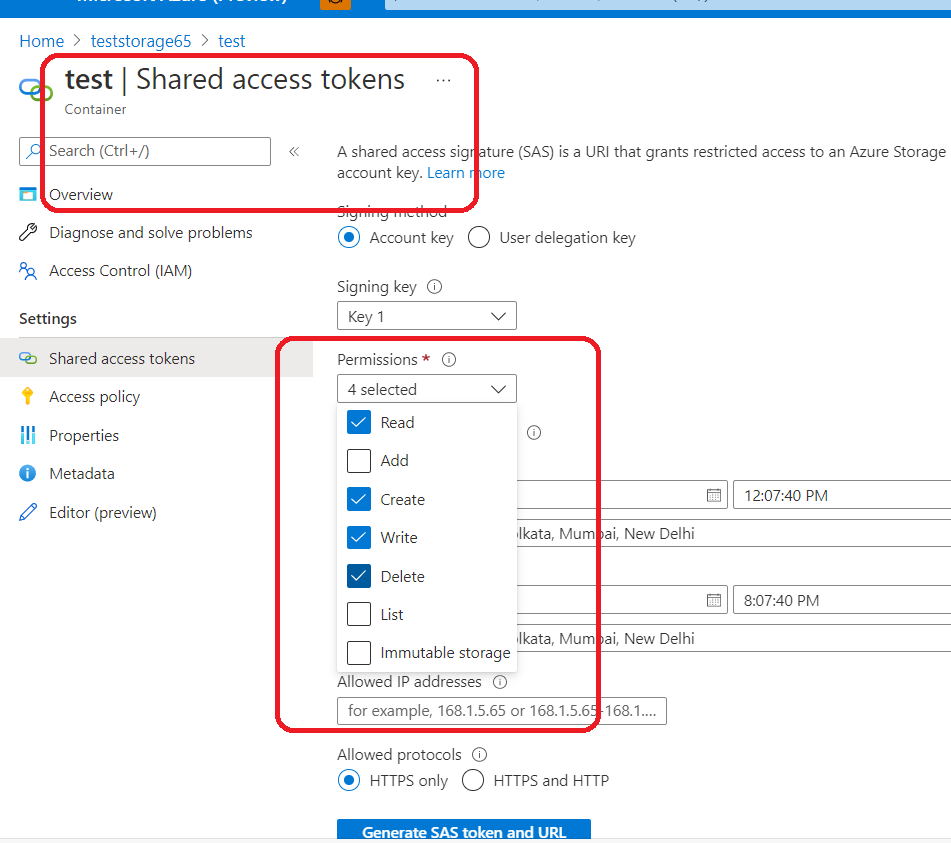
const string sasToken = "SAS Token";
StorageCredentials storageCredentials = new StorageCredentials(sasToken);
const string accountName = "teststorage65";//Account Name
const string blobContainerName = "test";
const string blobName = "test.txt";
const string myFileLocation = @"Local Path ";
var storageAccount = new CloudStorageAccount(storageCredentials, accountName, null, true);
CloudBlobClient blobClient = storageAccount.CreateCloudBlobClient();
CloudBlobContainer blobContainer = blobClient.GetContainerReference(blobContainerName);
//blobContainer.CreateIfNotExists();
CloudBlockBlob cloudBlob = blobContainer.GetBlockBlobReference(blobName);
cloudBlob.UploadFromFile(myFileLocation);
As you already know You can use the Storage connection string to connect with Storage.
CloudStorageAccount storageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse("Connection string");
CloudBlobClient blobClient = storageAccount.CreateCloudBlobClient();
CloudBlobContainer container = blobClient.GetContainerReference("test");
Your application needs to access the connection string at runtime to authorize requests made to Azure Storage.
You have several options for storing your connection string Or SAS Token
1) You can store your connection string in an environment variable.
2) An application running on the desktop or on a device can store the connection string in an app.config or web.config file. Add the connection string to the AppSettings section in these files.
3) An application running in an Azure cloud service can store the connection string in the Azure service configuration schema (.cscfg) file. Add the connection string to the ConfigurationSettings section of the service configuration file.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-configure-connection-string