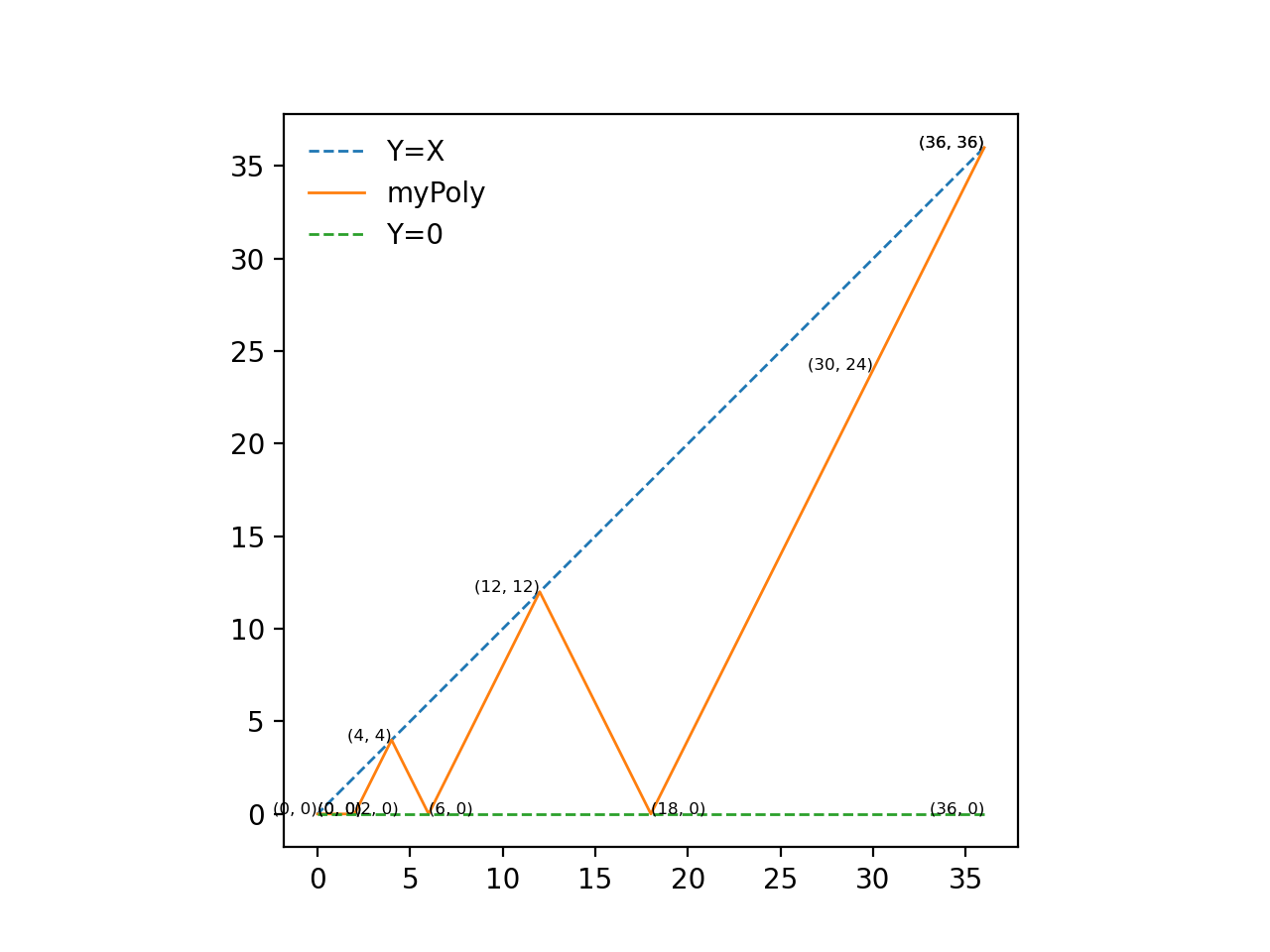
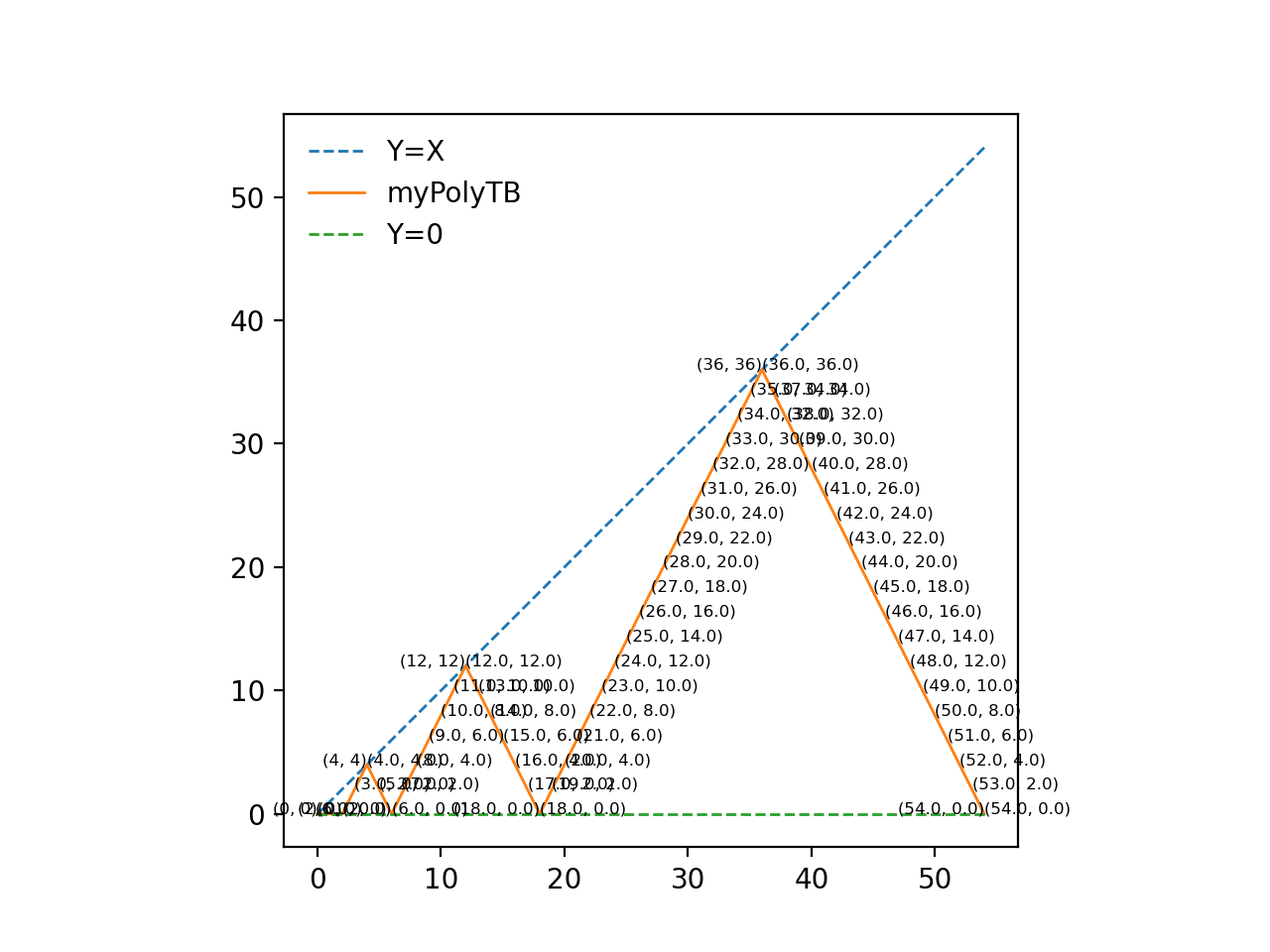
Can I define a line function in one line because it is regular?
graph orenge line : myPoly
Conditions :
The image oscillates between Y=0 and Y=X.
The slope of the line is 2 or -2.
You can start with (2,0).
I want
①Is it possible to define the following part def myPolyY(Ho,myX): in one line?
②Can you do it piecewise or in series?
from sympy import *
var('x y')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def myPolyY(Ho,myX):
myY=0
xx=[x[0] for x in Ho]
yy=[x[1] for x in Ho]
for i in range(len(xx)-1):
if xx[i] <= myX & myX<= xx[i 1]:
myY= (yy[i 1]-yy[i])/(xx[i 1]-xx[i])* (myX - xx[i]) yy[i]
return myY
def myPolyDef(nMax):
myPoly=[[0,0],[2,0]]
i=2
ans = solve([y - x,
y - myPoly[i-1][1] - 2 * (x - myPoly[i-1][0])], [x, y])
myPoly=myPoly [[ans[x], ans[y]]]
i=1
for j in range(nMax):
i=i 1
ans=solve([y-0,y-myPoly[i][1] 2*(x-myPoly[i][0])],[x,y])
myPoly=myPoly [[ans[x],ans[y]]]
i=i 1
ans=solve([y-x,
y-myPoly[i ][1]-2*(x-myPoly[i ][0])], [x,y])
myPoly=myPoly [[ans[x],ans[y]]]
return myPoly
def myPolyPlot(Ho,myLabel,myLinestyle):
plt.plot([x[0] for x in Ho],[x[1] for x in Ho], mec='none', ms=4, lw=1, label=myLabel,linestyle=myLinestyle)
for i in range(len(Ho)):
if i % 2==0:
myPos='right'
else:
myPos='left'
plt.text(Ho[i][0], Ho[i][1], '({x}, {y})'.format(x=Ho[i][0], y=Ho[i][1]),
fontsize=6, horizontalalignment=myPos)
return
def main():
# myN=4
myN=2
myX=30
myPoly=myPolyDef(myN)
myY=myPolyY(myPoly,30)
# matplotlib
myH=max(list(map(lambda x: max(x), myPoly)))
plt.axes().set_aspect('equal')
plt.text(myX,myY, '({x}, {y})'.format(x=myX, y=myY),
fontsize=6, horizontalalignment='right')
myPolyPlot([[myH,myH],[0,0]],'Y=X','--')
myPolyPlot(myPoly,'myPoly','-')
myPolyPlot([[myH, 0],[0,0]],'Y=0','--')
plt.legend(frameon=False, fontsize=10, numpoints=1, loc='upper left')
plt.savefig('myPoly.png', dpi=200)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
(2022-03-03) I used log.
from sympy import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
var('x y')
def myCal_PolyTopBottom(myT):
myPolyTB = [[0, 0], [2, 0]]
for x in range(myT):
xt = 4*(3**x)
yt = 4*pow(3, int(log(xt // 2, 3)))
myPolyTB = myPolyTB [[xt , yt ]]
myPolyTB = myPolyTB [[xt yt * 0.5, 0.0]]
return myPolyTB
def myCal_PolyXYN(myPolyTB,myXmax):
myPolyXYN = [[0, 0], [2, 0]]
for x in range(3, int(myXmax) 1):
y=myCal_PolyXYi(myPolyTB,x)
myPolyXYN = myPolyXYN [[float(x), y]]
return myPolyXYN
def myCal_PolyXYi(Ho,myX):
xx=[x[0] for x in Ho]
yy=[x[1] for x in Ho]
for i in range(len(xx)-1):
if xx[i] <= myX & myX<= xx[i 1]:
myY= (yy[i 1]-yy[i])/(xx[i 1]-xx[i])* (myX - xx[i]) yy[i]
return myY
def myPlot_Poly(Ho,myLabel,myLinestyle):
plt.plot([x[0] for x in Ho],[x[1] for x in Ho],
mec='none', ms=4, lw=1, label=myLabel,linestyle=myLinestyle)
return
def myPlot_Text(Ho,myPos):
for i in range(len(Ho)):
plt.text(Ho[i][0], Ho[i][1], '({x}, {y})'.format(x=Ho[i][0], y=Ho[i][1]),
fontsize=6, horizontalalignment=myPos)
return
def main():
myT=3
myPolyTB=myCal_PolyTopBottom(myT)
myH=max(list(map(lambda x: max(x),myPolyTB)))
myPolyN=myCal_PolyXYN(myPolyTB,myH)
# matplotlib
plt.axes().set_aspect('equal')
myPlot_Text(myPolyTB,'right' )
myPlot_Text(myPolyN ,'left' )
myPlot_Poly([[myH,myH],[0,0]],'Y=X' ,'--')
myPlot_Poly( myPolyTB ,'myPolyTB','-' )
myPlot_Poly([[myH, 0],[0,0]],'Y=0' ,'--')
plt.legend (frameon=False, fontsize=10, numpoints=1, loc='upper left')
# plt.savefig('myPoly.png', dpi=200)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
CodePudding user response:
If you look at the first triangle, it is easy to see that the equation can be expressed as
y = 4 - 2 * abs(4-x)
More generally, each triangle has a top value, and the corresponding equation is
y = top - 2 * abs(top-x)
Then, for each coordinate x, we have to determine the value of the corresponding top
top = 4 * pow(3, int(log(x//2,3)))
from math import *
myPoly=[[0,0],[2,0]]
for x in range(3, 37):
val = 4 * pow(3, int(log(x//2,3)))
y = val - 2 * abs(x - val)
myPoly = myPoly [[x,y]]