When I run the following code:
from tkinter import *
rows = []
for i in range(3):
cols = []
for j in range(3):
e = Entry(relief=RIDGE)
e.grid(row=i, column=j, sticky=NSEW)
e.insert(END, '%d.%d' % (i, j))
cols.append(e)
rows.append(cols)
def onPress():
for row in rows:
for col in row:
col.get(),
print()
Button(text='Calculate', command=onPress).grid()
mainloop()
I get a 3 by 3 grid where I can enter six numbers. I want to incorporate the following code into the above code:
x = r_1[0] r_2[0] - r_3[0]
y = r_1[1] r_2[1] - r_3[1]
z = r_1[2] r_2[2] - r_3[2]
num = x y - z
list = [x, y, z]
i = 0
while (i < 3):
fin = 2000*list[i]*num
print(fin)
i = i 1
Such that when I run the code I get an output of three numbers displayed below the "Calculate" button in the grid. The r_1[0] denotes the first entry in the first row of the grid, the r_2[0] denotes the second entry in the first row of the grid etc.
I'm not sure how to make the code work.
CodePudding user response:
You could try something like below:
# Change our import statement to import the tkinter module as tk
import tkinter as tk
# Define our function for the action to complete on our button press
def onPress(rootInstance, output):
# Get our input values as a dictionary
inputVals = rootInstance.children
# Set the values for x, y, and z
x = float(inputVals['entry00'].get()) float(inputVals['entry01'].get()) - float(inputVals['entry02'].get())
y = float(inputVals['entry10'].get()) float(inputVals['entry11'].get()) - float(inputVals['entry12'].get())
z = float(inputVals['entry20'].get()) float(inputVals['entry21'].get()) - float(inputVals['entry22'].get())
# Get our output label string variables
outputList = output
# Process the x, y, and z variables
num = x y - z
# Set our x, y, and z variables to a list
list = [x, y, z]
# Iterate over our list and outputList variables in a zipped fashion
for i, j in zip(list, outputList):
fin = 2000*i*num
# Set the value of the output equal to our computed value
j.set(str(fin))
# Update our root instance
rootInstance.update_idletasks()
# Define our main method
def main():
# Create our root tkinter instance
root = tk.Tk()
# Specify size of window
root.geometry("650x200")
# Create our input fields
rows = []
for i in range(3):
cols = []
for j in range(3):
e = tk.Entry(root, relief=tk.RIDGE, name=('entry' str(i) str(j)))
e.grid(row=i, column=j, sticky=tk.NSEW)
e.insert(tk.END, '%d.%d' % (i, j))
cols.append(e)
rows.append(cols)
# Add a section for our output below:
outputText = tk.Label(root, text = "Output", font="Arial 11 bold").grid(row=4, column=0)
out1 = tk.StringVar()
out1.set("-")
out2 = tk.StringVar()
out2.set("-")
out3 = tk.StringVar()
out3.set("-")
output1 = tk.Label(root, textvariable = out1, name='output1').grid(row=5, column=0)
output2 = tk.Label(root, textvariable = out2, name='output2').grid(row=5, column=1)
output3 = tk.Label(root, textvariable = out3, name='output3').grid(row=5, column=2)
# Add a lambda function to our button command below, so it only executes when we click the button
button_calc = tk.Button(root, text='Calculate', command= lambda: onPress(root, [out1, out2, out3])).grid(row=3, column=0)
root.update()
# Call the main loop of our tkinter instance
root.mainloop()
# Execute our "main" function below
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
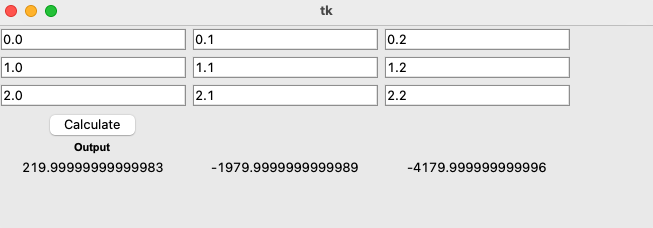
That should yield some output like below:
For reference, the thread below talk more about using tkinter with text variables:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-setting-and-retrieving-values-of-tkinter-variable/