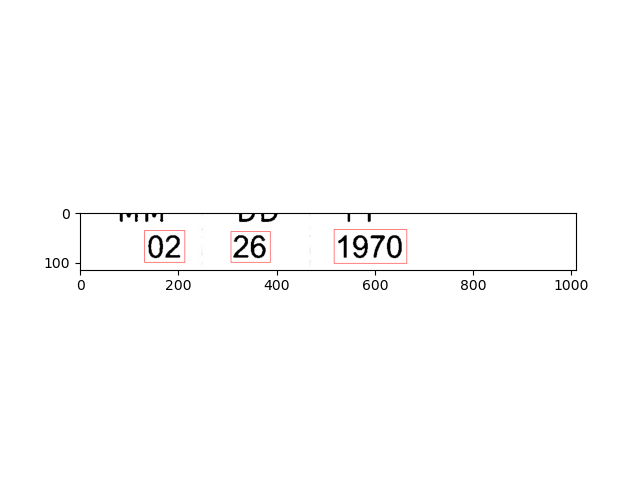
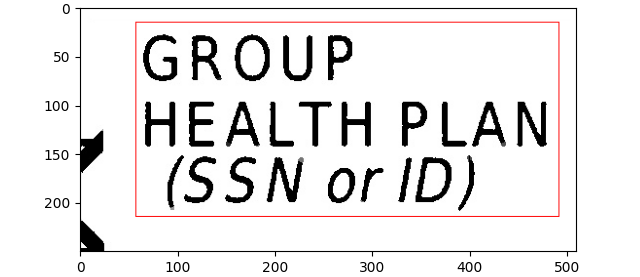
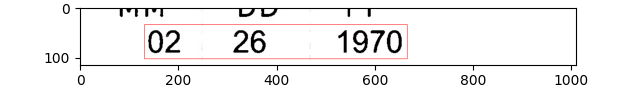
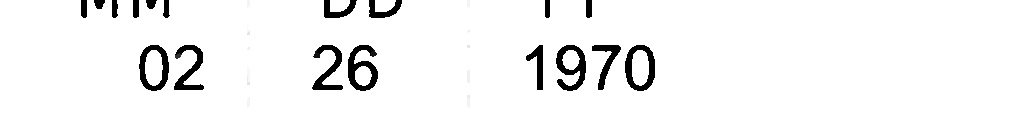I am using easyocr to detect the text in the image. The method gives the output bounding box. The input images are shown below
Image 1
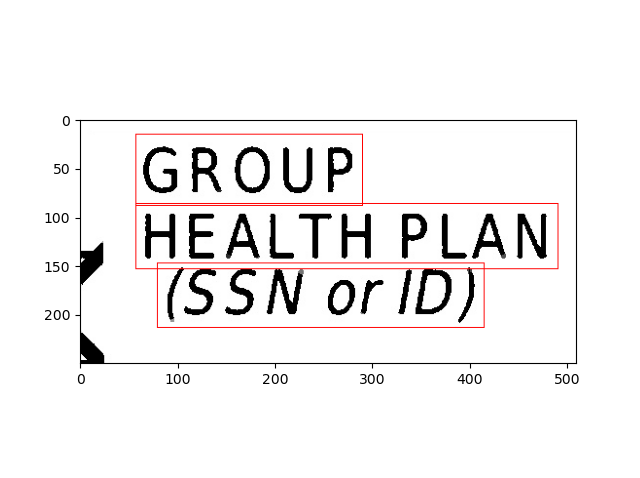
The output image is obtained using the code below.
But I want to draw a Single/Bigger bounding box that includes all the text and Crop the image with respect to the bounding box and Delete the remaining unwanted area or text.
Here is the code attached Requirements
pip install pytesseract
pip install easyocr
Run the code using python main.py -i image1.jpg
# USAGE
# python localize_text_tesseract.py --image apple_support.png
# python localize_text_tesseract.py --image apple_support.png --min-conf 50
# import the necessary packages
from pytesseract import Output
import pytesseract
import argparse
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
import easyocr
from PIL import ImageDraw, Image
def remove_lines(image):
result = image.copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
# Remove horizontal lines
horizontal_kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (40,1))
remove_horizontal = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, horizontal_kernel, iterations=2)
cnts = cv2.findContours(remove_horizontal, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[0] if len(cnts) == 2 else cnts[1]
for c in cnts:
cv2.drawContours(result, [c], -1, (255,255,255), 5)
# Remove vertical lines
vertical_kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (1,40))
remove_vertical = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, vertical_kernel, iterations=2)
cnts = cv2.findContours(remove_vertical, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[0] if len(cnts) == 2 else cnts[1]
for c in cnts:
cv2.drawContours(result, [c], -1, (255,255,255), 5)
plt.imshow(result)
plt.show()
return result
# construct the argument parser and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True,
help="path to input image to be OCR'd")
ap.add_argument("-c", "--min-conf", type=int, default=0,
help="mininum confidence value to filter weak text detection")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
reader = easyocr.Reader(['ch_sim','en']) # need to run only once to load model into memory
# load the input image, convert it from BGR to RGB channel ordering,
# and use Tesseract to localize each area of text in the input image
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
image = remove_lines(image)
results = reader.readtext(image)
#print('originalresult',results)
low_precision = []
for text in results:
if text[2]<0.45: # precision here
low_precision.append(text)
for i in low_precision:
results.remove(i) # remove low precision
print(results)
#import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
image2 = Image.fromarray(image)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image2)
for i in range(0, len(results)):
p0, p1, p2, p3 = results[i][0]
draw.line([*p0, *p1, *p2, *p3, *p0], fill='red', width=1)
plt.imshow(np.asarray(image2))
plt.show()
CodePudding user response:
After removal of low precision results you can combine all the valid points into a single 2D array and use cv2.boundingRect to get the bounding box.
Code:
points = []
for result in results:
points.extend(result[0])
rect = cv2.boundingRect(np.array(points))
x, y, w, h = rect
image2 = image.copy()
cv2.rectangle(image2, (x, y), (x w, y h), (255, 0, 0), 1)
plt.imshow(image2)
plt.show()
Images:
And to crop the text use this line:
image_cropped = image[y:y h, x:x w]
or if more precise cropping is needed:
mask = np.zeros_like(image)
# grayscale or color image
color = 255 if len(mask.shape) == 2 else mask.shape[2] * [255]
# create a mask
for result in results:
cv2.fillConvexPoly(mask, np.array(result[0]), color)
# mask the text, and invert the mask to preserve white background
image_masked = cv2.bitwise_or(cv2.bitwise_and(image, mask), cv2.bitwise_not(mask))
image_cropped = image_masked[y:y h, x:x w]