I am trying to generate a plot for double integral using python, matplotlib. X and Y ranges are defined and Z is the double integral of X and Y.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy
from scipy.integrate import dblquad
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={"projection": "3d"})
def function_I(x, y):
return np.sin(x)*np.cos(y/5)
#Make data
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
Z = scipy.integrate.dblquad(function_I, -5, 5, -5, 5)
# plot the surface
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.show()
line
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
gives
AttributeError: 'tuple' object has no attribute 'ndim'
some similar question provided solutions related to .shape and .reshape? Doesn't make a whole lot sense. Any comments appreciated!
CodePudding user response:
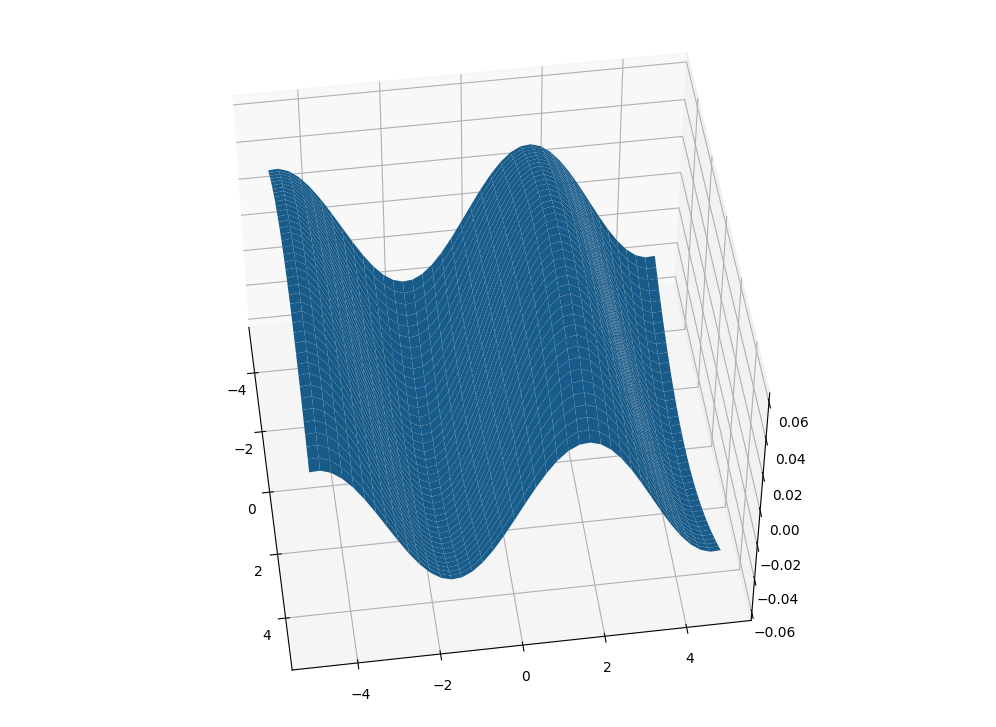
dblquad(function_I, -5, 5, -5, 5) calculates the integral of one complete area, so resulting in a single value.
The following approach intents to calculate the integral for each little patch between successive coordinates. And then draw a surface using the mean XY position of each patch.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.integrate import dblquad
def function_I(x, y):
return np.sin(x) * np.cos(y / 5)
# Make data
X = np.linspace(-5, 5, 41)
Y = np.linspace(-5, 5, 41)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
Z = np.zeros_like(X)
for i in range(1, X.shape[0]):
for j in range(1, X.shape[1]):
Z[i, j], _ = dblquad(function_I, X[i - 1, j - 1], X[i, j], Y[i - 1, j - 1], Y[i, j])
# plot the surface
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={"projection": "3d"})
ax.plot_surface((X[:-1, :-1] X[1:, 1:]) / 2, (Y[:-1, :-1] Y[1:, 1:]) / 2, Z[1:, 1:])
plt.show()