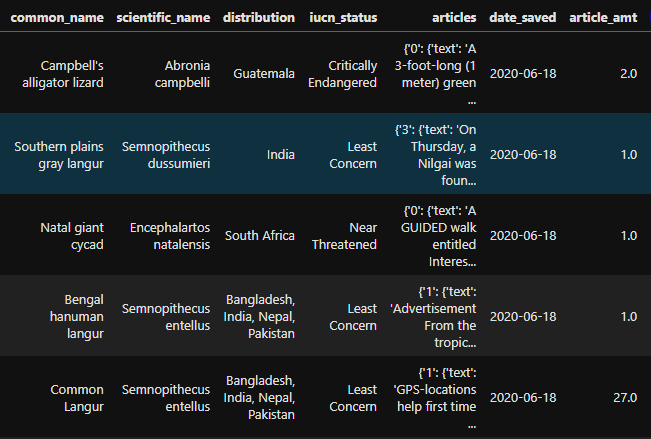
I have a dataframe with one column, "articles", that has dictionaries as values. Some dictionaries contain multiple values. You can see the number of 'text' values in the dictionary of the articles column in the column titled "article_amt".
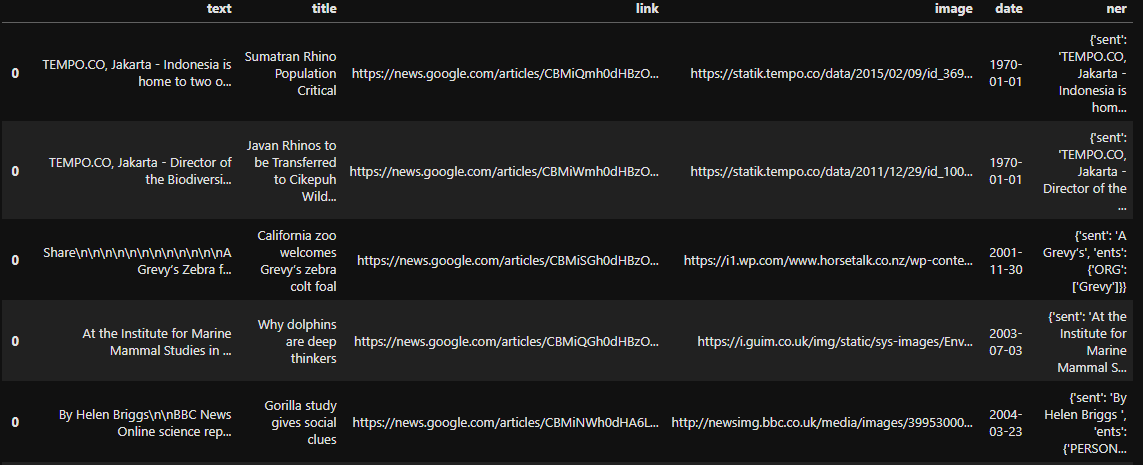
I want to explode that column so that each key of the dictionary is its own column in the dataframe. I have been able to convert the articles column into its own dataframe, but I no longer have the species information when I do so, which I need. Here is an example of the dataframe of just the "articles" column
My goal is to end up with a dataframe with all of the columns listed in both screencaps, with repeating rows for the species-specific information for as many articles as each species has. I have browsed some similar questions online but they result in unnecessary columns for me or placing the keys from the articles column as the index. My data is rather large so I can't paste a sample in here but a simplified example should be:
data = {'age': [59, 18, 63],
'sample': [({'0': {'a':'yes', 'b': 'no'}, '1':{'a': 'maybe', 'b': 'NA'}}), ({'0': {'a':'no', 'b': 'yes'}}), ({'0': {'a':'no', 'b': 'no'}, '1':{'a': 'no', 'b': 'yes'}, '2':{'a': 'yes', 'b': 'yes'}})],
'date': ['2022-09-29', '2022-08-29', '2022-07-29']}
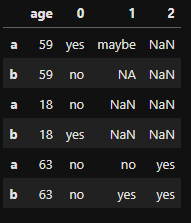
I have tried the following solution:
pd.concat(t['sample'].apply(pd.DataFrame).tolist(),
keys=t["age"]).reset_index(level="age")
And get the following:
I want the keys, "a" and "b" to be included as columns
CodePudding user response:
explode the dict values in sample then create a intermediate dataframe from the exploded values and join back with original dataframe
s = df['sample'].map(dict.values).explode()
df.drop(columns=['sample']).join(pd.DataFrame([*s], s.index))
Result
age date a b
0 59 2022-09-29 yes no
0 59 2022-09-29 maybe NA
1 18 2022-08-29 no yes
2 63 2022-07-29 no no
2 63 2022-07-29 no yes
2 63 2022-07-29 yes yes
CodePudding user response:
You can try to rework the output of json_normalize:
out = df.drop(columns='sample').join(
pd.json_normalize(df['sample'])
.pipe(lambda d: d.set_axis(d.columns.str.split('.', expand=True), axis=1))
.stack().rename_axis([None, 'new']).reset_index(-1)
)
Output:
age date new 0 1 2
0 59 2022-09-29 a yes maybe NaN
0 59 2022-09-29 b no NA NaN
1 18 2022-08-29 a no NaN NaN
1 18 2022-08-29 b yes NaN NaN
2 63 2022-07-29 a no no yes
2 63 2022-07-29 b no yes yes